10 Best Clean Energy Solutions for a Sustainable Future?
As the world grapples with climate change, the need for clean energy solutions has never been more urgent. These solutions offer a pathway to a sustainable future. They promise reduced emissions and a healthier planet. However, this journey is not without its challenges. Each clean energy solution presents unique advantages and limitations.
Imagine a world powered by wind, solar, and hydroelectric energy. Wind turbines and solar panels dominate the landscape. Yet, questions arise about their efficiency and environmental impact. Transitioning to these technologies requires investment and infrastructure changes.
Moreover, renewable energy sources must compete with fossil fuels. This competition complicates the shift to clean energy solutions. It’s crucial to examine the practicality of implementing these technologies in diverse regions. The experience from various countries shows that local context matters. Ultimately, embracing clean energy solutions calls for thoughtful consideration and community engagement.

Top Solar Technologies Revolutionizing Clean Energy Production
The shift towards clean energy is gaining momentum, with solar technologies leading the way. These innovations offer new avenues for sustainable energy production. One emerging technology is bifacial solar panels. They capture sunlight from both sides, increasing energy output. Research shows that these panels can improve efficiency by 20% compared to traditional models.
Another development is the integration of solar tracking systems. These systems follow the sun's path throughout the day, maximizing energy capture. They can involve complex mechanics, which may raise reliability concerns. However, the potential increase in energy generation makes them worth exploring. It’s essential to assess their long-term viability in various environments.
Moreover, perovskite solar cells are gaining attention for their cost-effectiveness. They have the potential to reduce manufacturing costs significantly. Yet, their stability and long-term performance need further research. As we push for cleaner energy solutions, it's crucial to focus on not just technological advances, but also the challenges that come with them. Balancing innovation with sustainability must remain our goal.
10 Best Clean Energy Solutions for a Sustainable Future
| Energy Solution | Type | Efficiency (%) | Cost ($/kWh) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar PV | Photovoltaic | 15-22 | 0.05-0.08 | Low emissions, can reduce carbon footprint |
| Wind Turbines | Wind Energy | 35-45 | 0.01-0.02 | Minimal pollution, wildlife impact considered |
| Hydropower | Hydroelectric | 35-45 | 0.02-0.05 | Can disrupt ecosystems, but low emissions |
| Geothermal | Geothermal Energy | 10-20 | 0.05-0.08 | Low emissions, land use impact |
| Biomass | Bioenergy | 20-25 | 0.07-0.10 | Can reduce waste, but can release CO2 |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cells | Hydrogen Energy | 40-60 | 0.05-0.15 | Zero emissions at use, but production effects |
| Tidal Energy | Ocean Energy | 28-40 | 0.15-0.25 | Low emissions, but can affect marine life |
| Nuclear Fusion | Nuclear Energy | ~80 | Not yet available | Very low emissions, but safety concerns |
| Energy Storage (Batteries) | Energy Storage | Dependent on technology | 0.15-0.30 | Can improve grid efficiency, recycling concerns |
Innovative Wind Energy Solutions for Sustainable Power Generation

Wind energy is becoming a crucial component of sustainable power generation. It accounts for approximately 7% of global electricity production, according to the International Energy Agency. Innovative solutions are emerging, making wind energy more accessible and efficient.
Advanced turbine designs are enabling energy generation even at low wind speeds. For example, some modern turbines can capture energy from winds as low as 2 meters per second. This opens up new locations for wind farms, especially in regions previously deemed unsuitable. Additionally, offshore wind farms are gaining traction, providing greater energy yields. Research shows that the potential for offshore wind energy could power over 18 million homes in the U.S. alone.
**Tip**: Consider local wind patterns before setting up wind turbines. Some areas might show higher energy potential than others.
However, not all wind energy solutions come without challenges. Issues like noise and impact on wildlife need addressing. Furthermore, the visual aspect of wind farms can lead to local opposition. Ongoing research on blade technology aims to reduce noise and increase lifespan, but it requires time and investment.
**Tip**: Engage with local communities early in the planning process. Addressing concerns can lead to better acceptance.
The transition to wind energy remains a work in progress. Technology continues to evolve, driving efficiency and acceptance. The journey towards a sustainable future is indeed complex but necessary.
Advancements in Energy Storage Systems for Renewables Optimization
Advancements in energy storage systems are critical for optimizing renewable energy. Recent studies indicate that energy storage can reduce renewable energy curtailment by up to 50%. This is significant, especially with wind and solar, which are variable sources of energy. For instance, a large-scale deployment of batteries has potential savings of $300 billion globally by 2030.
Current lithium-ion technology dominates the market, but alternatives are emerging. Solid-state batteries, for example, promise longer life and higher energy density. Research shows they can increase energy capacity by 30% compared to conventional batteries. Yet, production challenges remain. Costs are still high, and scalability is a concern. Many researchers believe breakthroughs in materials could offer solutions.
Despite the progress, integrating energy storage with the grid remains an issue. Grid stability is paramount. It needs to handle the influx of renewable sources and their storage methods effectively. Energy supply must align with demand. Inconsistent production from renewables can lead to instability. Investing in smart grid technologies may help bridge this gap, but hurdles still linger. More data and development are necessary.
Emerging Hydrogen Fuel Technologies for a Greener Future
Hydrogen fuel has gained attention as a major player in the clean energy revolution. This emerging technology could drastically reduce greenhouse gas emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, hydrogen could account for 18% of the world's energy demand by 2050. This potential is driven by ongoing advancements in production methods and fuel cell technologies.
Hydrogen can be produced from various sources, including renewable energy like wind and solar. Electrolysis, a process that separates water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, offers a green route. However, the current cost of hydrogen production remains a challenge. In 2022, the cost of green hydrogen production ranged from $3 to $7 per kilogram, depending on the source. Achieving cost-effectiveness is crucial for widespread adoption.
Despite its promise, there are hurdles to overcome. Hydrogen storage and transport present technical challenges that require innovative solutions. Currently, most hydrogen is transported via pipelines or trucks, which can be inefficient. The industry must focus on minimizing these logistical barriers. There is also a need for infrastructure investment to support this technology. The path to a greener future is not smooth, and continuous efforts are necessary to address these imperfections.
10 Best Clean Energy Solutions for a Sustainable Future
Sustainable Practices in Bioenergy for Environmental Conservation
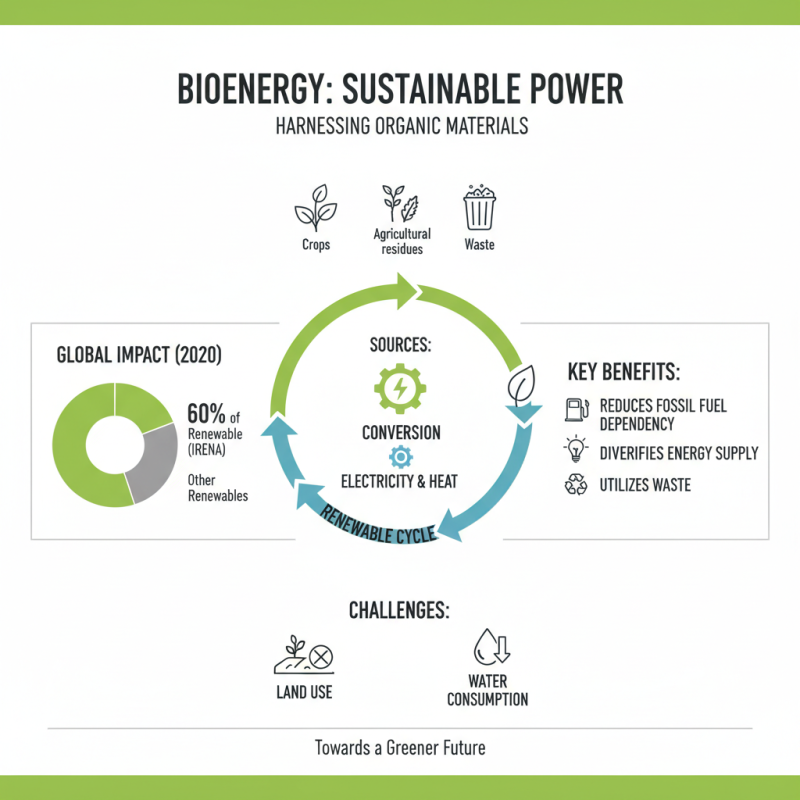
Bioenergy has emerged as a pivotal solution in sustainable practices. It involves harnessing organic materials for energy production. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), bioenergy constituted approximately 60% of renewable energy in 2020. This percentage highlights its importance in reducing fossil fuel dependency. Crops, agricultural residues, and waste are essential sources. However, challenges like land use and water consumption must be addressed.
Sustainable bioenergy practices focus on minimizing environmental impact. For example, using waste materials can reduce landfill issues and lower greenhouse gas emissions. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that proper management of bioenergy resources could lead to a 30% reduction in carbon emissions. Yet, there are concerns about monoculture practices affecting biodiversity. Critics urge more research into sustainable sourcing to prevent resource depletion.
Investing in advanced technologies like anaerobic digestion can help. These methods convert organic waste into energy and fertilizers. They offer a closed-loop system that benefits both the environment and the economy. Yet, the financial barriers to such technologies are significant. Many communities lack the initial funding needed to make these systems viable. Exploring innovative financing solutions remains crucial for broader success in sustainable bioenergy practices.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Energy Solutions for a Sustainable Future You Need to Know
-

How to Transition to Clean Energy: A Complete Guide for Homeowners
-

Exploring the Future of Clean Energy Sources Transforming Our Planet
-

Understanding Renewable Energy in a Changing World
-

Innovative Approaches in Renewable Energy Engineering for a Sustainable Future
-

2025 Top 10 Renewable Energy Sources Transforming Our Future
