Top Energy Solutions Driving Sustainable Innovation Today?
The world is at a pivotal moment in its energy transition. As the effects of climate change become increasingly apparent, innovative energy solutions are essential. These solutions combine technology and sustainability, aiming to reduce carbon footprints while powering economies.
Today, we see numerous initiatives emerging in renewable energy. Solar, wind, and bioenergy are leading the charge. Each offers unique advantages, but challenges remain. The implementation of these energy solutions often lacks uniformity. Some regions excel while others lag behind.
Moreover, the investment in energy storage technologies is crucial. The ability to harness excess energy can transform our approach to power consumption. However, infrastructure still poses hurdles. As we explore these topics, it’s clear that the journey toward sustainable energy is complex and requires collective reflection.

Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies and Their Impact
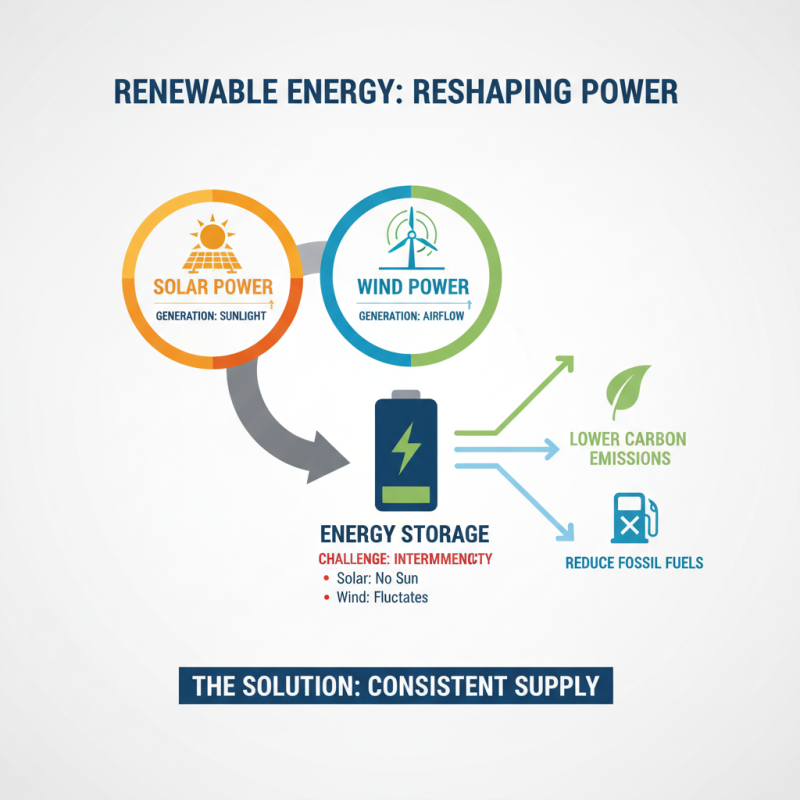
Renewable energy technologies are reshaping the way we generate electricity. Solar panels and wind turbines are at the forefront of this transformation. These innovations are lowering carbon emissions and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Yet, challenges still exist. For instance, energy storage remains a critical barrier. Solar power generates energy only when the sun shines. Wind energy fluctuates. Solutions must address these inconsistencies.
Investments in battery technology are vital. Advancements in lithium-ion batteries enhance storage capabilities. However, this technology isn't without its issues. Mining for lithium can have environmental consequences. Efforts to develop sustainable mining practices are crucial.
Tips: Always evaluate the environmental impact of energy solutions. Look for technologies that prioritize sustainability. Engage with local energy policies to understand the best options for your region. Embrace continuous learning about renewable developments. Staying informed can help you support the right innovations.
The Role of Energy Storage Solutions in Sustainable Innovation
Energy storage solutions are crucial for driving sustainable innovation. They enhance the efficiency of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. These technologies capture excess energy produced during peak generation times. This energy is then stored for use when demand is high. For example, during sunny days, more solar energy is generated than needed. Energy storage helps balance supply and demand.
However, challenges remain. The current storage options may not be sufficient for large-scale needs. Battery technology is evolving, but it still faces limitations in cost, lifespan, and environmental impact. There are discussions about recycling old batteries, but these processes need improvement. Exploring alternative materials can reduce reliance on scarce resources.
Innovation in energy storage also opens doors to new ideas. It can lead to off-grid solutions, helping remote areas gain access to clean energy. This aspect of innovation must be carefully considered. As we push for sustainable progress, the path is not always clear. Each step requires reflection and adaptation to achieve true sustainability.
Smart Grid Technologies Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Management
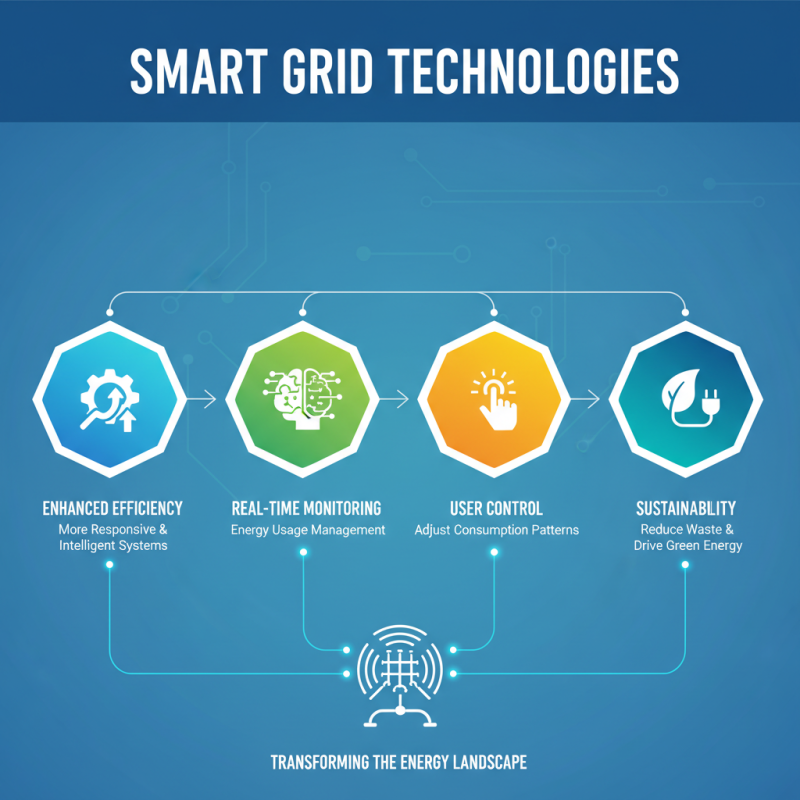
Smart grid technologies are transforming the energy landscape. They enhance energy efficiency, making systems more responsive and intelligent. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring and management of energy usage. Users can adjust consumption patterns, reducing waste and driving sustainability.
Many homes now utilize smart meters. These devices track energy use, providing insights that encourage better habits. However, not all consumers fully grasp their benefits. Education is needed to maximize the potential of smart grid technologies. Some users may still rely on outdated methods, missing out on savings.
Grid integration is another challenge. Renewable energy sources are gaining traction, but the grid must adapt. Balancing supply and demand is complex. Energy storage solutions are key, yet they are still costly. This leads to discussions about accessibility and equity in energy distribution. As we innovate, we must address these gaps.
Emerging Trends in Carbon Capture and Utilization for Cleaner Energy
Carbon capture and utilization (CCU) is gaining traction as a key player in today’s sustainable energy landscape. It offers a pathway to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions while producing useful products. By trapping CO2 from industrial processes, it can be repurposed for various applications. One exciting trend is using captured carbon to produce fuels. This approach can potentially close the carbon loop. Innovations in this area are evolving rapidly.
Another significant trend is mineralization. This process transforms CO2 into stable carbonates, which can be used in construction materials. It not only reduces atmospheric CO2 but also offers a way to create sustainable infrastructure. However, the technology still faces challenges. Scaling these methods is complex and costly. The logistics of transporting captured CO2 can be another hurdle for widespread adoption.
Moreover, public perception and policy support often lag behind technical advances. Many people are unaware of the benefits of CCU. Educating the community is essential for acceptance. There’s also a need for regulatory frameworks that support these initiatives. Balancing innovation with real-world application remains a critical issue. Despite these shortcomings, the potential of CCU to drive cleaner energy solutions is undeniable.
Top Energy Solutions Driving Sustainable Innovation Today? - Emerging Trends in Carbon Capture and Utilization for Cleaner Energy
| Technology | Description | Carbon Capture Rate (%) | Applications | Current Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Air Capture | Technology that captures CO2 directly from the atmosphere. | 90% | Climate control, synthetic fuels | Pilot |
| Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) | Captures CO2 from industrial sources and stores it underground. | 80% | Power generation, cement industry | Commercial |
| Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) | Combines biomass energy production with CCS. | 95% | Energy generation, waste management | Demonstration |
| Mineralization | Processes CO2 into stable minerals for long-term storage. | 85% | Construction materials, geological storage | Research |
| Carbon Utilization | Converts captured CO2 into usable products. | Variable | Chemicals, fuels, plastics | Emerging |
Policy Frameworks Promoting Sustainable Energy Innovations Worldwide
The global shift toward sustainable energy hinges on effective policy frameworks. Regulations and incentives shape how renewable technologies develop. Countries that prioritize clean energy show significant progress. Strong policies encourage investments and innovation. For instance, subsidies for solar energy installation often lead to increased adoption. These frameworks can create jobs and stimulate local economies.
However, challenges remain in implementing these policies. Some regions struggle with outdated regulations that stifle growth. Others face resistance from traditional energy sectors. Policymakers must address these obstacles head-on. Transparency is critical. Stakeholders should engage in open dialogue to refine these frameworks. Assumptions about energy systems need questioning.
Building a sustainable future is complex. Policymakers must navigate economic interests and environmental goals. Balancing these forces is no easy task. Encouraging cross-border cooperation can amplify successes. Innovations in energy storage and efficiency must be supported. There's room for improvement, even within successful programs. The journey toward sustainable energy is ongoing, requiring constant adaptation and commitment.
Top Energy Solutions Driving Sustainable Innovation Today
Related Posts
-

Top Energy Engineering Trends to Watch in 2025: Innovations and Opportunities
-

Why Energy Engineering is Key to Achieving a Sustainable Future with Global Energy Demand Expected to Rise by 25 Percent by 2040
-

Exploring the Future of Sustainable Energy Systems for a Greener Planet
-

Innovative Power Generation Techniques for a Sustainable Future
-

Transforming Tomorrow with Innovative Sustainable Energy Systems and Cutting Edge Technologies
-

Exploring the Future of Sustainable Energy Systems for a Greener Planet
