What is a Hybrid Generator and How Does It Work?
In recent years, the concept of a hybrid generator has gained significant traction. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in renewable energy, stated, "Hybrid generators represent the future of sustainable power." These innovative systems combine two or more energy sources, such as solar and diesel, to create a more efficient energy solution.
The hybrid generator works by optimizing the strengths of each energy source. For example, solar panels can harness sunlight during the day while a diesel generator kicks in during cloudy weather or high demand. This synergy not only improves efficiency but also reduces reliance on fossil fuels. However, the integration of multiple power sources can present challenges. Selecting the right components and managing the energy flow requires careful planning and expertise.
Despite the promising benefits, some users may experience issues with system complexity. Installation and maintenance can also pose challenges. The hybrid generator is a step towards a more sustainable future, but it’s important to address these obstacles thoughtfully. There is still much to learn about maximizing its potential.

Definition of a Hybrid Generator and Its Key Components
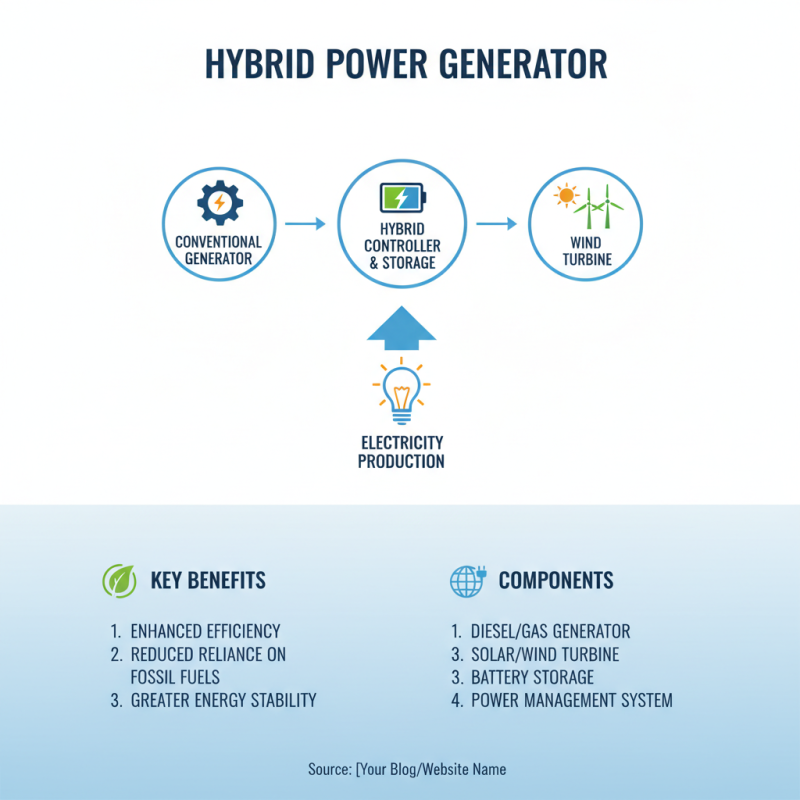
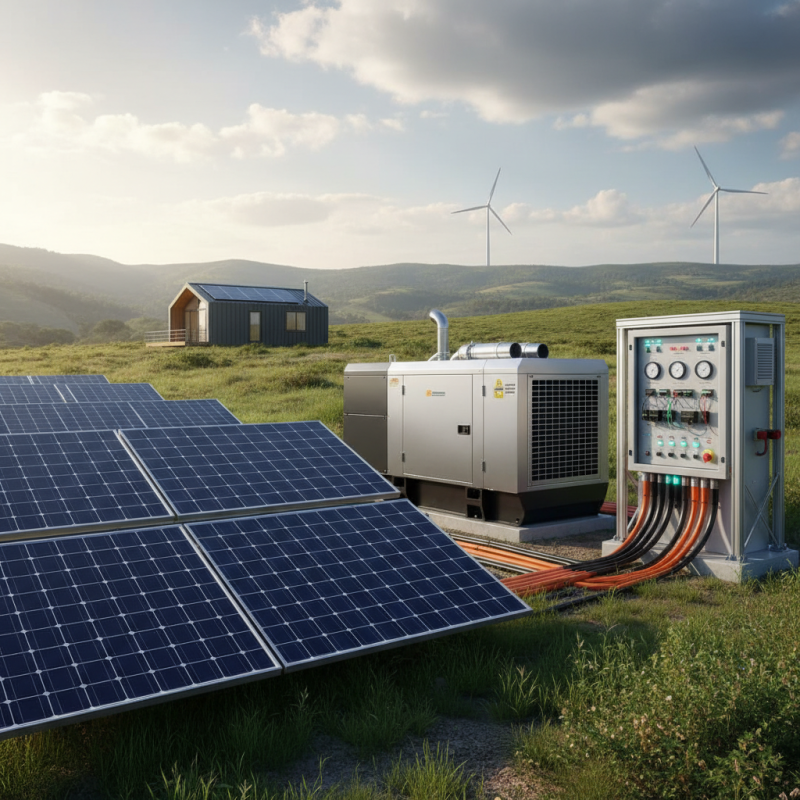
A hybrid generator combines multiple energy sources to produce electricity. It typically integrates conventional generators with renewable options like solar panels or wind turbines. This design aims to enhance efficiency and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Key components include an internal combustion engine, a generator, batteries, and an energy management system. The engine can run on diesel or gasoline, while batteries store excess energy. The energy management system regulates how power is distributed between sources.
One challenge in hybrid generators is balancing the inputs effectively. Sometimes, the system may not switch sources seamlessly. This can lead to inefficiencies. Adjusting the energy management settings might help, but it requires constant monitoring. Understanding these components ensures better use and reveals areas needing improvement. Hybrid generators offer a promising step toward sustainable energy solutions, yet their operation is complex.
Types of Energy Sources Used in Hybrid Generators
Hybrid generators combine different energy sources to produce electricity. These systems primarily rely on renewable energies, like solar and wind power, but they also incorporate conventional fuels. The integration of diverse resources helps to optimize energy output and enhance reliability. According to a report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), hybrid systems can be up to 25% more efficient than standalone systems.
Solar panels are common in hybrid generators. They convert sunlight into electricity. Wind turbines can also be part of the mix. They generate power from wind energy. The combination of these sources provides a consistent energy flow. Data indicates that hybrid systems can reduce fuel consumption by over 30%. This reduction is crucial for lowering operational costs and decreasing emissions.
**Tip:** If considering a hybrid system, evaluate local climate and resources. The efficiency of solar panels in sunny regions will vastly differ from wind turbines in breezy areas.
Batteries often link these systems. They store excess energy for later use. This flexibility can greatly improve a generator’s performance. However, managing energy storage can be complicated. Overcharging or underutilization of batteries can lead to inefficiencies. Regular monitoring is essential for optimal operation.
How Hybrid Generators Operate: A Step-by-Step Explanation
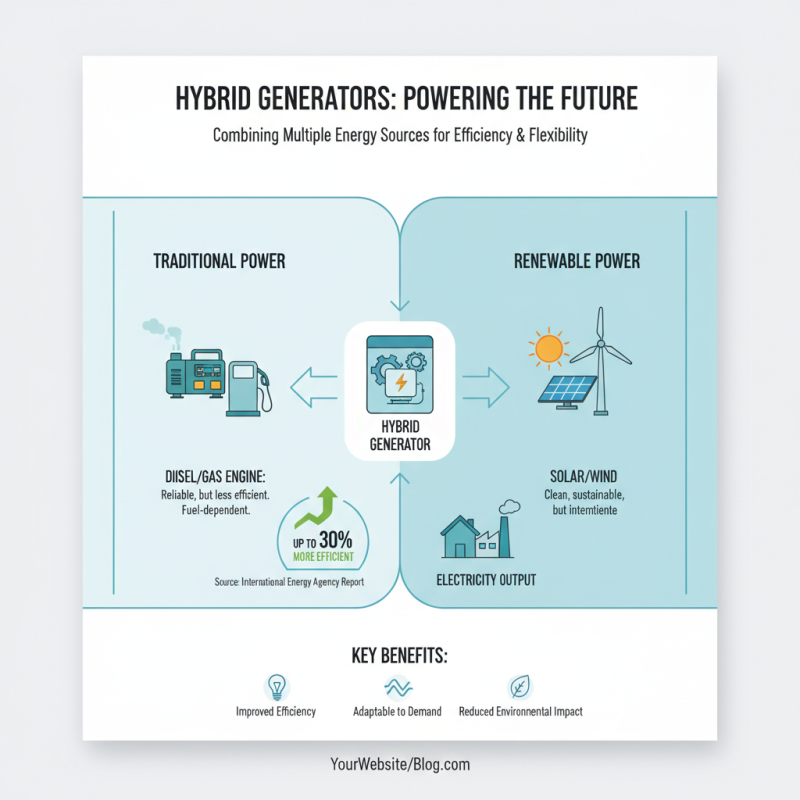
Hybrid generators combine multiple energy sources to produce electricity. Typically, they use a diesel or gas engine alongside renewable sources like solar or wind. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, hybrid systems can improve efficiency by up to 30%. This dual setup allows flexibility in energy generation, adapting to various demands.
The operation of a hybrid generator involves integrating these energy sources. During high demand, the engine kicks in. When demand is low, renewable sources take over. This balance is crucial. A study published in the Renewable Energy journal highlights that hybrid systems can significantly reduce fuel consumption. However, transitioning to a hybrid model requires substantial investment and planning. This can pose challenges, especially for smaller operations.
While hybrid generators promise efficiency, there are drawbacks. The complexity of managing multiple energy sources can confuse operators. They need proper training to maximize benefits. Additionally, ongoing maintenance can be costly and time-consuming. Adopting a hybrid generator is not a straightforward solution; it demands careful consideration. Understanding the operational intricacies is vital to ensure optimal performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Hybrid Generators
Hybrid generators combine different energy sources to produce electricity. They often use solar panels and diesel generators together. This combination can be efficient, but it also has its pros and cons.
One advantage is reliability. A hybrid generator can provide power even when the sun isn’t shining. This is crucial for remote areas or during emergencies. Additionally, using renewable energy sources reduces fuel costs. However, the initial investment for setting up a hybrid system can be substantial. It may not suit all budgets easily.
Another downside is maintenance. Keeping both solar panels and generators functioning optimally requires regular checks. This can be time-consuming and may lead to unexpected costs. Users must weigh these factors carefully. Balancing the benefits of sustainability versus potential inconveniences may require thoughtful consideration.
Hybrid Generator Efficiency and Fuel Usage Comparison
This chart illustrates the energy contribution from various sources in a hybrid generator system. Solar power is shown to contribute the most at 50%, followed by wind power at 30%, and diesel generators at 20%. This distribution highlights the potential for renewable energy integration in hybrid systems.
Applications of Hybrid Generators in Various Industries
Hybrid generators combine different power sources. They seamlessly integrate renewable energy, like solar or wind, with traditional generators. This technology is gaining traction across various industries. For example, in construction, hybrid systems can reduce fuel costs by up to 40%. This is significant in lowering operational expenses on large projects.
In the telecommunications sector, hybrid generators improve reliability. They ensure uninterrupted power supply to remote cell sites. A report from the Global Telecommunications Association highlights that hybrid systems can enhance energy efficiency by over 30%. However, there are challenges. Installation costs can be a barrier for small companies. Not every site is ideal for hybrid solutions.
The maritime industry is also exploring hybrid generators. These systems can reduce emissions significantly. A study by the International Maritime Organization reported that hybrid power can create a 20% reduction in greenhouse gases. Despite these benefits, maintenance can be complex and may require specialized training. The technology is evolving, and not all hybrid setups are optimized for every application.
Related Posts
-

Why Sustainable Energy Systems Are Essential for a Greener Future
-

10 Best Strategies for a Successful Energy Transition in 2023
-

Why Energy Engineering is Key to Achieving a Sustainable Future with Global Energy Demand Expected to Rise by 25 Percent by 2040
-

2025 Top 10 Renewable Energy Sources Transforming Our Future
-

Innovative Power Generation Techniques for a Sustainable Future
-

What is an Energy Storage System and How Does It Work for Your Needs
